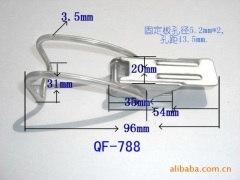
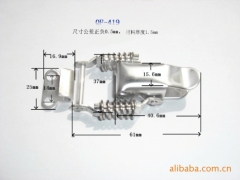
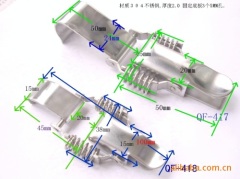
|
Ningbo Mingzhi Stainless Product Co.,Ltd
|
China Stainless steel strip China Stainless steel coil
| Price: | 10000.0~11000.0 USD |
| Payment Terms: | T/T,L/C,D/A,D/P, |
| Place of Origin: | Zhejiang, China (Mainland) |
|
|
|
| Add to My Favorites | |
| HiSupplier Escrow |
Product Detail
The characteristics and application of 409 stainless steel:
409 stainless steel, the most inexpensive models (England), usually used in automobile
Precision - stainless steel packed with all metal and atmospheric oxygen for reaction, the formation of oxide film on the surface. Unfortunately, the iron oxide in the form of ordinary carbon steel on oxidation, rust continues to expand, eventually forming holes. You can use paint or oxidation-resistant metal (for example, zinc, nickel and chromium) plating to ensure the carbon steel surface, but, as everyone knows, this protection is only a thin film. So the magnet is not up.
Stainless steel usually in the matrix organization is divided into:
1, ferritic stainless steel. From 12% to 30%. Its corrosion resistance, toughness and can increase the welding with chromium increases the amount of resistance to chloride stress corrosion is superior to other types of stainless steel. 2, austenitic stainless steel. Chromium is more than 18%, still contain 8% of nickel and a small amount of molybdenum, titanium, nitrogen and other elements. Comprehensive performance is good, resistant to a variety of medium corrosion.
3, AUSTENITIC FERRITIC duplex stainless steel. Both austenite and ferrite stainless steel and has the advantages of, superplasticity.
4, martensitic stainless steel. High strength, plasticity and poor weldability.
5, precipitation hardening stainless steel. With good formability and good weldability, high strength materials can be used in the nuclear industry, aviation and aerospace industry.
Components can be divided according to Cr (SUS400), Cr-Ni system (SUS300), cr-mn-ni (SUS200) and the precipitation hardening systems (SUS600).
Related Search
Stainless Steel Coil Strip
Coil Stainless Steel
Stainless Steel Coil
Stainless Steel In Coil
Stainless Steel Coil Sheet
Polished Stainless Steel Coil
More>>